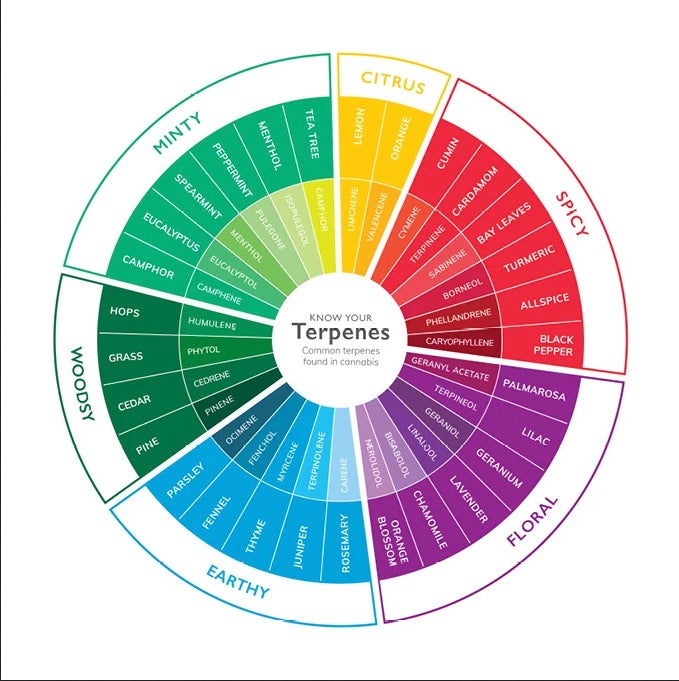
Terpenes are the aromatic compounds that determine the taste and smell of plants and some animals. The reason why a lemon tastes and smells like a lemon is due to these compounds we call Terpenes.
Most manufacturers use isolated terpenes, sinlge terpene compounds to create the flavors and scents of many everyday products, such as perfumes, body products, and even foods. Herbanology uses a complex array of terpens, as occurs naturally in the cannabis plant, to showcase the wide array of aromas that a cannabis plant creates naturally.
Terpenes play a vital role in plants. In some plants, terpenes attract pollinators, while in other plants, they cause a strong reaction to repel predators, such as insects or foraging animals. Mint repelling mosquitos is a good example.
Some terpenes play a protective role in the plant, helping the plant to recover from damage; others act as a part of the plant’s immune system to keep away infectious germs.
Some people also use the term terpenoids. However, terpenes and terpenoids are not the same.
Terpenes are the natural form of these compounds when they are in the live plant. As a plant dries and cures — in the production of cannabis, for example — the terpenes oxidize and become terpenoids.
Terpenes are primarily responsible for the smell and taste of most plants and some animal compounds. However, some terpenes may also act on the endocannabinoid system in the body in a similar way to cannabinoids. The key difference is that the body absorbs and uses these compounds in different ways.
Many terpenes are bioactive, which means they may affect the body. This effect will vary based on the concentration of the terpene itself and how a person uses it.
Because terpenes produce vibrant smells, they form the basis of many essential oils and are an integral part of many alternative therapies, such as aromatherapy. Inhaling the scents from some plants and essential oils may affect a person’s mood and stress levels.
Some people believe that terpenes will affect or enhance the high a person gets from using cannabis. This is known as the
Some research backs up these claims. For instance, a review in
There is plenty of medical research on isolated terpenes themselves, and some may even make their way into medical use. A study in Chemico-Biological Interactionsnotes that many terpenes have demonstrated beneficial effects on the body and could serve as alternative medicine or therapies.
Excerpts taken from medical news today:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/what-are-terpenes?c=219923216833#effects
While there are many terpenes in the natural world, scientists have only studied a handful.
Examples of better-known terpenes include:
Limonene
Limonene is a common terpene that most people can recognize by its scent. As the name suggests, limonene gives the rinds of fruits such as lemons and oranges their citrusy smell.
A study in Chemico-Biological Interactions notes that limonene contains the following therapeutic properties:
- anti-inflammatory
- antioxidant
- antiviral
- antidiabetic
- anticancer
Limonene appears to modulate the way certain immune cells behave, which may protect the body from a range of disorders. Limonene is also safe for people to take as a supplement.
Pinene
Pinene is another naturally abundant terpene. There are two forms of pinene: a-pinene and b-pinene. Pinene provides the fresh, bright scent of many plants, including pine needles, rosemary, and basil. Pinene may also have some therapeutic benefits.
Shirin-yoku, which means “forest bathing,” is a Japanese therapy that involves taking leisurely walks in the forest, soaking up the atmosphere, and enjoying the scent. Shirin-yoku may have
A study in Acta Salus Vitae notes that the amount of pinene in the air of a healthy forest is enough to be therapeutic. Pinene acts as a bronchodilator, allowing more air into the lungs. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect and may fight against some infectious germs when inhaled.
Linalool
Linalool is most abundant in the lavender plant and gives the flower its rich scent. Linalool is one of the more important compounds in aromatherapy and is responsible for the calming effect many people get when smelling lavender or its essential oil.
A study in Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces notes that linalool may affect the body in a variety of ways due to a range of properties, including:
- anti-inflammatory
- antimicrobial
- neuroprotective
- antidepressant
- anticancer
- anti-anxiety
Linalool does appear to act on the body, but researchers must study its effects further to understand how people can use it to benefit their health.
Myrcene
Myrcene is a terpene commonly found in plants such as hops, lemongrass, and thyme. The flowers of the cannabis plant also contain myrcene.
Myrcene is a powerful antioxidant. One
Another study in mice found that myrcene had a similar protective effect in heart tissue. The researchers note that myrcene may be a useful alternative treatment after ischemic stroke.
However, it is important to bear in mind that these studies used very high concentrations of myrcene, up to 200 milligrams (mg) per kilogram (kg) (mg/kg) of weight.
Another
Beta-caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene exists in many herbs and vegetables, such as cloves and black pepper.
Similarly to other terpenes, beta-caryophyllene may have an anti-inflammatory effect on the body that could reduce pain levels in some people.
In one
Humulene
Humulene is a key component of the hop plant. Other plants, such as clove and ginger, also contain it.
One study in
Another study in Food and Chemical Toxicology found that humulene may also have a protective effect in some cells. This protective effect could guard against cancer. However, this is just preliminary evidence, and researchers must continue to study the effects of humulene to back up these claims.
Other terpenes
The terpenes mentioned above are among the most abundant active terpenes that people are likely to come across. Some additional common terpenes include:
- geraniol
- terpinolene
- ocimene
- nerolidol
- phytol
Terpenes are the compounds responsible for the way most plants smell. They are abundant in cannabis and many other plants, fruits, and herbs.
They may play a role in the health and survival of the plants in which they exist.
In some cases, smelling specific essential oils, ingesting terpene-rich plants, or spending time in areas with high terpene content may provide some health benefits to humans.
Researchers must continue to study terpenes to understand their potential therapeutic and medicinal uses fully.